编写一个Buildroot 驱动模块
由于Buildroot 不支持ssh
故采用adb调试
adb连接
列出设备
adb devices
连接设备
adb shell
驱动模块编译(交叉编译)
驱动模块源码
#include <linux/module.h> /* 模块相关宏和函数 */
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk日志函数 *//* 加载函数(驱动入口),当驱动被 insmod 加载时自动执行 */
static int __init helloworld_init(void)
{printk("helloworld_init\r\n"); // 内核日志打印return 0; // 返回0代表加载成功
}/* 卸载函数(驱动出口),当驱动被 rmmod 卸载时自动执行 */
static void __exit helloworld_exit(void)
{printk("helloworld_exit\r\n");
}/* 下面这两行,告诉内核入口和出口分别是哪两个函数 */
module_init(helloworld_init);
module_exit(helloworld_exit);/* 这3个是模块信息声明 */
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2"); /* 模块许可证 */
MODULE_VERSION("1.0"); /* 模块版本,可选 */
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("helloworld Driver");/* 模块描述,可选,一般用于 lsmod 时显示 */
功能简单解释就是
加载驱动:打印helloworld_init
卸载驱动:打印helloworld_exit
找到交叉编译工具路径
find prebuilts -name "*gcc" -type f

一般在SDK路径下找
配置Makefile
# 目标架构
# RK3566 是 ARM64 架构
ARCH ?= arm64# 交叉编译工具链前缀
# 最终会使用:aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc / ld / objcopy 等
CROSS_COMPILE ?= aarch64-linux-gnu-# Linux 内核源码目录
# 必须是已经配置并且执行过 prepare/modules_prepare 的内核
#作用:告诉 Makefile 用哪个内核版本的源码和头文件进行编译链接。
KDIR := $(HOME)/Desktop/SDK/kernel# 当前外部模块源码所在目录
# 内核会在这个目录下查找 obj-m 指定的模块源码
PWD := $(shell pwd)# 要编译的外部内核模块
# hello_world.c → hello_world.ko
obj-m += hello_world.o# 默认目标:编译内核模块
all:# 调用内核源码目录下的 Makefile# M=$(PWD) 表示这是一个“外部模块”# ARCH / CROSS_COMPILE 指定目标架构和交叉编译器$(MAKE) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) \ARCH=$(ARCH) CROSS_COMPILE=$(CROSS_COMPILE) modules# 清理编译生成的中间文件
clean:$(MAKE) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) cleanPS:主要寻找配置
交叉编译工具链前缀:aarch64-linux-gnu-
Linux 内核源码目录路径:$(HOME)/Desktop/SDK/kernel
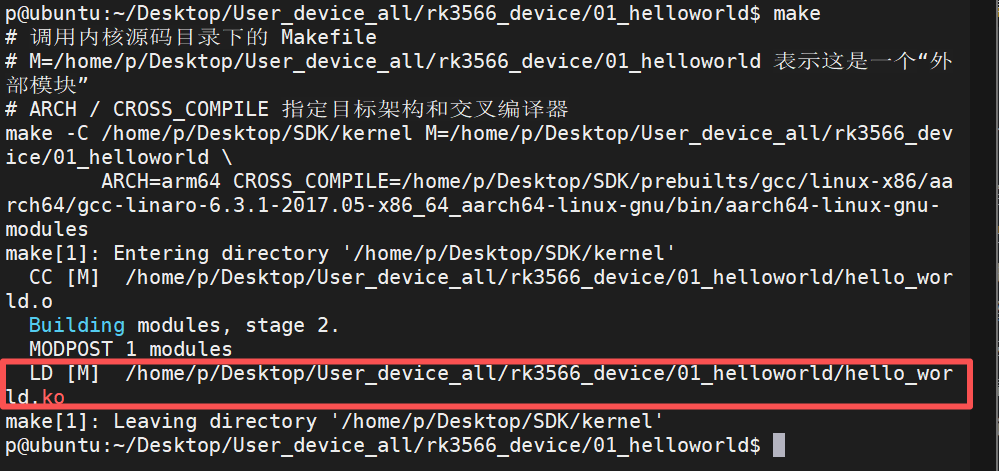
编译
make
模块输出路径
驱动测试
将驱动复制进rk3566板卡
使用ADB
如果ADB已经连上板卡,则先断开连接
exit
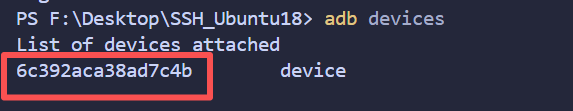
寻找板卡设备
adb devices
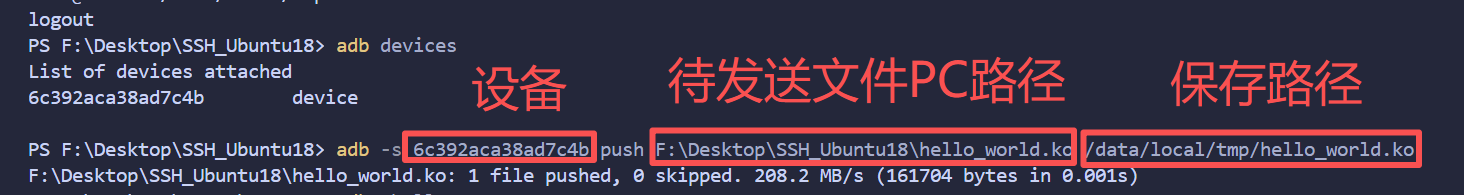
将本地的驱动模块文件发送到板卡
adb -s 6c392aca38ad7c4b push F:\Desktop\SSH_Ubuntu18\hello_world.ko /data/local/tmp/hello_world.ko
加载驱动模块:
insmod hello_world.ko
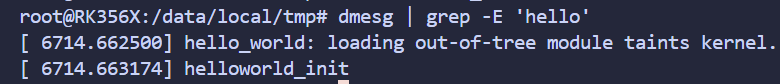
查看 驱动 相关日志
dmesg | grep -E 'hello'
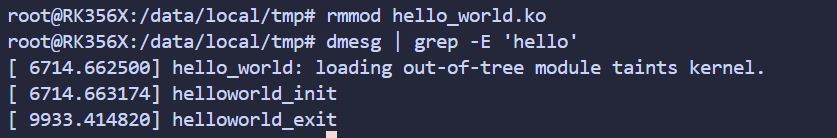
卸载模块驱动
rmmod hello_world.ko
查看 驱动 相关日志
dmesg | grep -E 'hello'